Parts of a Motherboard and Their Function
The Parts of a Computer Motherboard
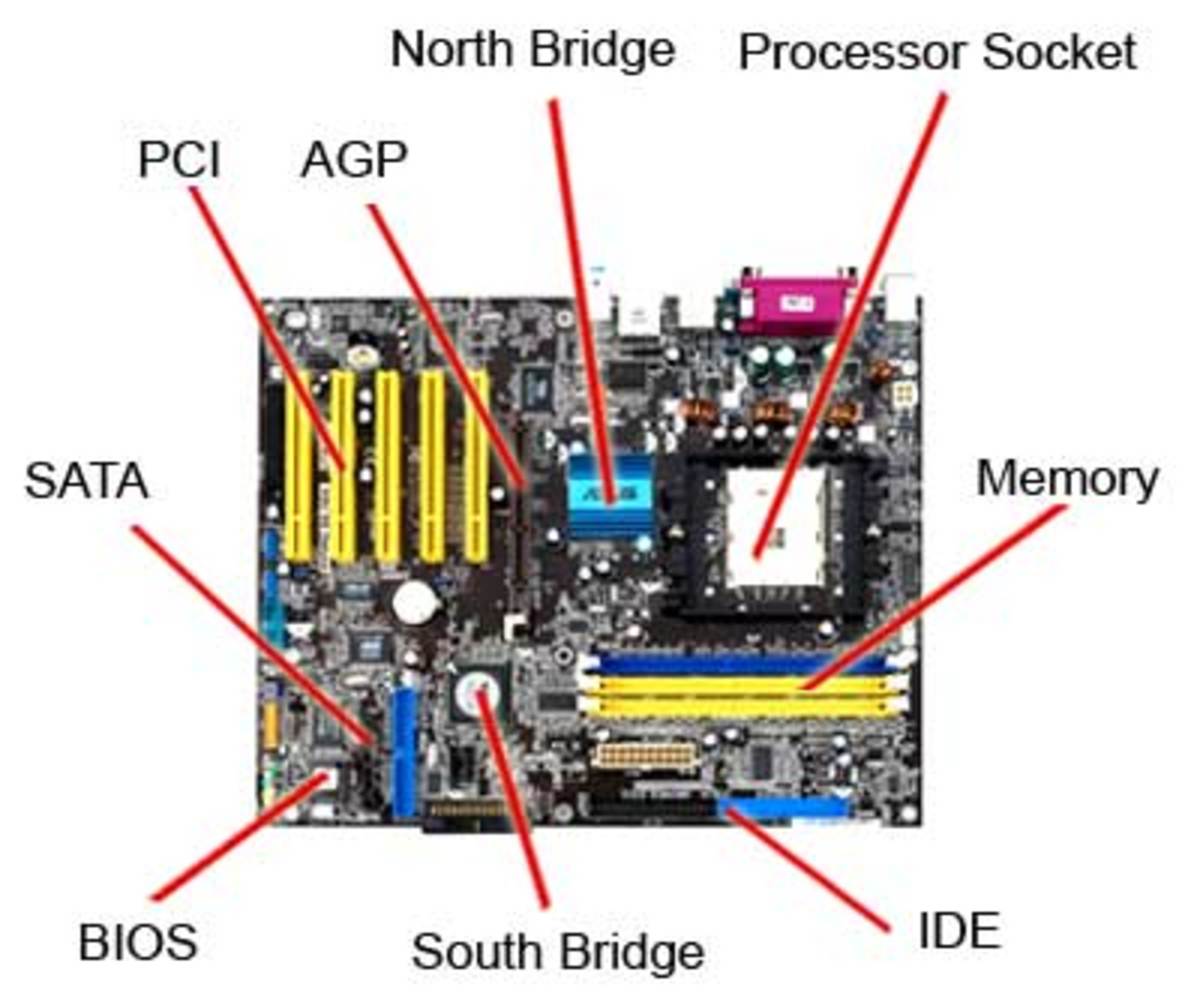
Major Motherboard Components and Their Functions
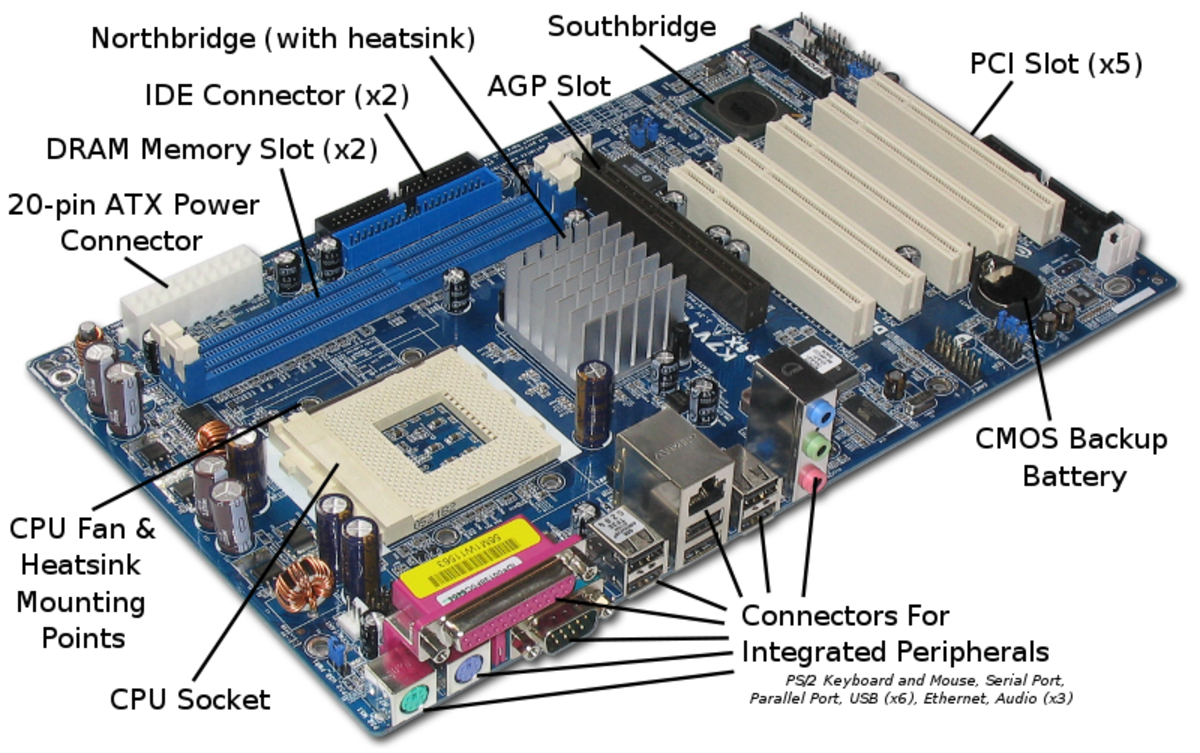
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
Also known as the microprocessor or the processor, the CPU is the computer's brain. It is responsible for fetching, decoding, and executing program instructions as well as performing mathematical and logical calculations.
The processor chip is identified by the processor type and the manufacturer. This information is usually inscribed on the chip itself. For example, Intel 386, Advanced Micro Devices (AMD) 386, Cyrix 486, Pentium MMX, Intel Core 2Duo, or iCore7.
Random Access Memory (RAM)
Random Access Memory, or RAM, usually refers to computer chips that temporarily store dynamic data to enhance computer performance while you are working.
In other words, it is the working place of your computer, where active programs and data are loaded so that any time time the processor requires them, it doesn't have to fetch them from the hard disk.
Random access memory is volatile, meaning it loses its contents once power is turned off. This is different from non-volatile memory, such as hard disks and flash memory, which do not require a power source to retain data.
Basic Input/Output System (BIOS)
BIOS stands for Basic Input/Output System. BIOS is a "read only" memory, which consists of low-level software that controls the system hardware and acts as an interface between the operating system and the hardware. Most people know the term BIOS by another name—device drivers, or just drivers. BIOS is essentially the link between the computer hardware and software in a system.
All motherboards include a small block of Read Only Memory (ROM) which is separate from the main system memory used for loading and running software. On PCs, the BIOS contains all the code required to control the keyboard, display screen, disk drives, serial communications, and a number of miscellaneous functions.
The system BIOS is a ROM chip on the motherboard used during the startup routine (boot process) to check out the system and prepare to run the hardware. The BIOS is stored on a ROM chip because ROM retains information even when no power is being supplied to the computer.
Complimentary Metal Oxide Semiconductor Random Access Memory (CMOS RAM)

Motherboards also include a small separate block of memory made from CMOS RAM chips which is kept alive by a battery (known as a CMOS battery) even when the PC’s power is off. This prevents reconfiguration when the PC is powered on.
CMOS devices require very little power to operate.
The CMOS RAM is used to store basic Information about the PC’s configuration for instance:-
- Floppy disk and hard disk drive types
- Information about CPU
- RAM size
- Date and time
- Serial and parallel port information
- Plug and Play information
- Power Saving settings
Other Important data kept in CMOS memory is the time and date, which is updated by a Real Time Clock (RTC).
Cache Memory

Cache memory is a small block of high-speed memory (RAM) that enhances PC performance by pre-loading information from the (relatively slow) main memory and passing it to the processor on demand.
Most CPUs have an internal cache memory (built into the processor) which is referred to as Level 1 or primary cache memory. This can be supplemented by external cache memory fitted on the motherboard. This is the Level 2 or secondary cache.
In modern computers, Levels 1 and 2 cache memory are built into the processor die. If a third cache is implemented outside the die, it is referred to as the Level 3 (L3) cache.
Expansion Bus

An expansion bus is an input/output pathway from the CPU to peripheral devices and it is typically made up of a series of slots on the motherboard. Expansion boards (cards) plug into the bus. PCI is the most common expansion bus in a PC and other hardware platforms. Buses carry signals such as data, memory addresses, power, and control signals from component to component. Other types of buses include ISA and EISA.
Expansion buses enhance the PCs capabilities by allowing users to add missing features in their computers by slotting adapter cards into expansion slots.
Chipsets
A chipset is a group of small circuits that coordinate the flow of data to and from a PC's key components. These key components include the CPU itself, the main memory, the secondary cache, and any devices situated on the buses. A chipset also controls data flow to and from hard disks and other devices connected to the IDE channels.
A computer has got two main chipsets:
- The NorthBridge (also called the memory controller) is in charge of controlling transfers between the processor and the RAM, which is why it is located physically near the processor. It is sometimes called the GMCH, for Graphic and Memory Controller Hub.
- The SouthBridge (also called the input/output controller or expansion controller) handles communications between slower peripheral devices. It is also called the ICH (I/O Controller Hub). The term "bridge" is generally used to designate a component which connects two buses.
Chipset manufacturers include SIS, VIA, ALI, and OPTI.
CPU Clock
The CPU clock synchronizes the operation of all parts of the PC and provides the basic timing signal for the CPU. Using a quartz crystal, the CPU clock breathes life into the microprocessor by feeding it a constant flow of pulses.
Switches and Jumpers
- DIP (Dual In-line Package) switches are small electronic switches found on the circuit board that can be turned on or off just like a normal switch. They are very small and so are usually flipped with a pointed object, such as the tip of a screwdriver, a bent paper clip, or a pen top. Take care when cleaning near DIP switches, as some solvents may destroy them. Dip switches are obsolete and you will not find them in modern systems.
- Jumper pins are small protruding pins on the motherboard. A jumper cap or bridge is used to connect or short a pair of jumper pins. When the bridge is connected to any two pins, via a shorting link, it completes the circuit and a certain configuration has been achieved.
Comments
Post a Comment